Business
How can robots help the disabled?
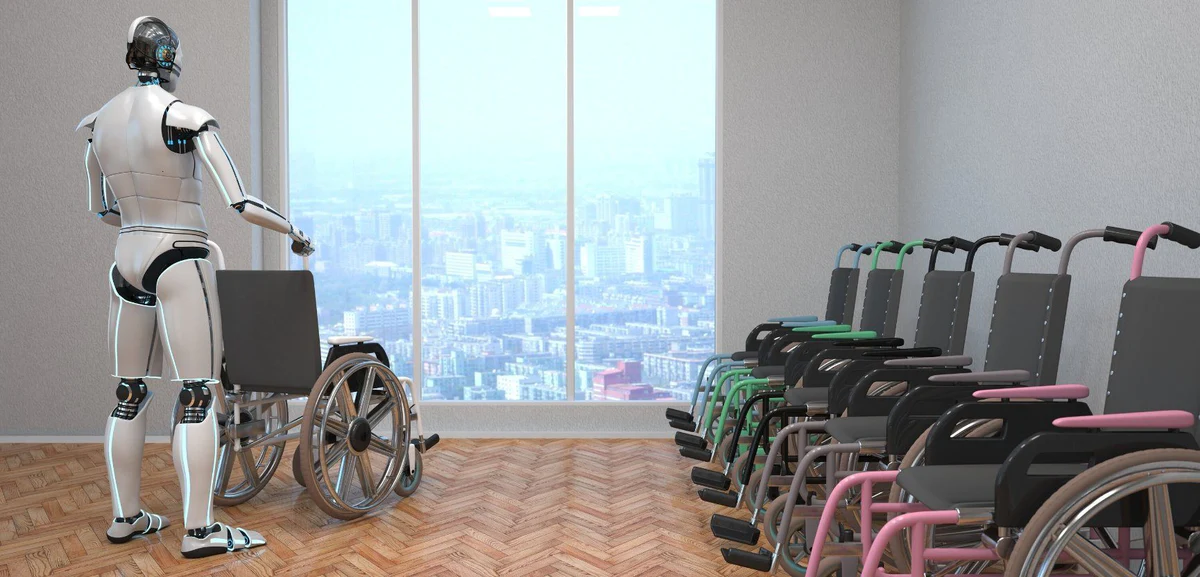

Robots have the potential to improve the lives of people with disabilities in numerous ways. With advances in technology, robotics has become more affordable, accessible, and versatile, enabling the development of a wide range of robotic devices that can assist people with disabilities in their daily activities. Here are some ways robots can help the disabled:
-
Mobility assistance
Mobility is a significant challenge for people with disabilities, particularly those with mobility impairments. Robots can provide mobility assistance in different ways. For instance, wheelchair robots can help people with mobility impairments move around independently, while exoskeletons can provide walking support to those with lower limb disabilities. These devices allow people with disabilities to engage in various activities, such as exercise, socializing, and work.
-
Assistance with daily living activities
Robots can help people with disabilities perform various daily living activities, such as cooking, cleaning, and grooming. For example, robotic arms can assist individuals with limited mobility in preparing meals or cleaning their homes. Similarly, robots can help people with visual impairments navigate their environment and perform other tasks, such as reading, writing, and typing.
-
Communication assistance
People with communication disabilities, such as those with speech and hearing impairments, face significant challenges in interacting with others. However, robots can provide assistance in this area. For example, robots with speech recognition and synthesis capabilities can help individuals with speech impairments communicate their thoughts and ideas. Similarly, sign language robots can translate spoken language into sign language and vice versa, enabling people with hearing impairments to communicate effectively.
-
Emotional support
Living with a disability can be challenging, and people with disabilities often experience emotional distress. Robots can provide emotional support to individuals with disabilities, such as those with autism or dementia. For example, companion robots can provide social interaction, offer emotional support, and help individuals with disabilities engage in various activities, such as playing games or watching movies.
-
Rehabilitation support
Robots can also help people with disabilities in their rehabilitation process. For example, robots can provide physical therapy for people with mobility impairments, such as stroke or spinal cord injury. Additionally, robots can assist individuals with neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis, in their rehabilitation process by providing feedback and support during exercises.
-
Education and training
Robots can assist in the education and training of people with disabilities. For instance, robots can provide language and literacy instruction to individuals with learning disabilities, such as dyslexia. Similarly, robots can teach individuals with autism social skills, such as taking turns and maintaining eye contact.
Conclusion
Robots have tremendous potential to improve the lives of people with disabilities. The use of robots in various areas, such as mobility assistance, daily living activities, communication assistance, emotional support, rehabilitation support, and education and training, can enable people with disabilities to lead more independent, productive, and fulfilling lives. However, it is essential to ensure that robots are designed to meet the unique needs and preferences of people with disabilities and that they are integrated into the overall care and support system to ensure their maximum benefits.
Business
Merced Craigslist: Your Ultimate Guide to Online Classifieds
These days, more and more people choose to do their shopping, selling, and socializing online through online marketplaces. Craigslist is one such site that has become very popular. In this post, we’ll look specifically at the Merced Craigslists and provide a full tutorial on how to use this popular online ads service.
Introduction to Merced Craigslist
Craigslist is a website where people may post adverts for things like jobs, apartments, needed goods, services, and more. It’s a place where individuals in the same region may go to advertise and locate things like jobs, apartments, and items. In particular, the residents of Merced, California can find what they’re looking for on Merced Craigslist.
What Is Craigslist?
Craigslist is a website where people may post adverts for things like jobs, apartments, needed goods, services, and more. It’s a place where individuals in the same region may go to advertise and locate things like jobs, apartments, and items. In particular, the residents of Merced, California can find what they’re looking for on Merced Craigslist.
The Popularity of Craigslist
The success of Craigslist can be attributed to how easy it is to use. Users may easily and swiftly locate the goods and services they need in their immediate area. Its simple layout promotes communication and does away with the necessity for lengthy user profiles.
Merced Craigslist: A Local Gem
The success of Craigslist can be attributed to how easy it is to use. Users may easily and swiftly locate the goods and services they need in their immediate area. Its simple layout promotes communication and does away with the necessity for lengthy user profiles.
How to Access Merced Craigslist
It’s simple to use Craigslist in Merced. You may either type “Merced Craigslists” into a search engine or go straight to the website. You can browse the available options and listings once you get to the site.
Navigating Merced Craigslist
Craigslist’s UI may look basic, but it really has many advanced options. Find exactly what you’re looking for and refine your results by price, proximity, and more. The intuitive layout of the site makes it simple to locate certain content.
Benefits of Using Merced Craigslist
There are a number of benefits to using the Merced Craigslists site. There are no hidden fees associated with There is a wide variety of sub-sections on the Merced Craigslists. You may look into available jobs, apartments, services, local events, and personal advertisements. Craigslist probably has a category for anything you’re looking for in Merced.
trade goods or services here on this website. The local focus ensures that you’ll have opportunities to interact with natives.
Common Categories on Merced Craigslist
There is a wide variety of sub-sections on the Merced Craigslist. You may look into available jobs, apartments, services, local events, and personal advertisements. Craigslist probably has a category for anything you’re looking for in Merced.
Safety Tips for Using Craigslist
While there are numerous upsides to using Craigslist, your safety should always come first. Avoid giving too much personal information with strangers you meet on the site, and always meet in a public area and follow your gut.
Avoiding Scams on Merced Craigslist
Scammers do operate on Merced Craigslists, just like they do on every other website. You should exercise extreme caution with bargains that sound too good to be true. Verify the listing’s validity and conduct any business dealings in person.
Selling on Merced Craigslist
Merced Craigslists allows users to post ads for goods and services with full descriptions and pictures. Build trust with potential purchasers by being open and honest in your listings.
Buying on Merced Craigslist
It’s important to do research and ask questions before making a purchase on Merced Craigslists. Make sure you meet in a public, safe place and bargain properly.
Merced Craigslist Community
In addition to being a marketplace, Craigslist is also a social network. Many people’s social and professional lives have been improved by this medium. Participating in neighborhood activities may be rewarding.
Success Stories from Merced Craigslist
Here are a few Merced, California, success stories about people who used Craigslist to find their ideal job, perfect apartment, or one-of-a-kind service.
Conclusion
The Merced area benefits greatly from having access to Craigslist. It facilitates communication, introduces people to one another, and serves as a marketplace for both buyers and sellers. However, users should always take precautions and put their own safety first when utilizing the service.
FAQ’s
Is using Merced Craigslist free?
Buyers and sellers alike may use Merced’s Craigslist for no cost at all.
How can I avoid scams on Merced Craigslist?
Avoid frauds by only meeting in public locations, listening to your gut, and checking listings to make sure they are legitimate.
Can I post multiple listings on Merced Craigslist?
You may, in fact, list many products or services.
What should I do if I encounter a suspicious listing on Merced Craigslist?
You should report any questionable ads to Craigslist moderators and refrain from communicating with the poster.
Are there any specific rules or guidelines for posting on Merced Craigslist?
Users are expected to abide by Craigslist’s terms of service and posting standards while making advertisements.
Business
What Can You Expect from a High-End London Office Space?

A high-end London office space is a premium workspace solution that offers exceptional services, amenities, and features That cater to the needs of modern-day businesses. These offices are designed to create an exceptional work environment that enhances productivity, creativity, and professionalism. Here are some of the things you can expect from a high-end London office space.
Location
One of the primary benefits of a high-end London office space is the location. These offices are often situated in some of the most prestigious and central locations in London, offering businesses easy access to the city’s major transportation hubs, business districts, and cultural landmarks. Prime locations such as Mayfair, the City of London, and Canary Wharf are popular choices for high-end offices.
Design and Layout
A high-end London office space is designed with style and comfort in mind. These offices feature contemporary architecture and modern design elements, offering businesses a professional and luxurious environment. The layout of these offices is often open-plan, providing ample space for collaboration and creativity while maintaining a sense of privacy.
Facilities and Amenities
High-end London office spaces offer a wide range of facilities and amenities designed to make work more enjoyable, convenient, and efficient. These include high-speed internet, conference rooms equipped with state-of-the-art audio and video technology, fully equipped kitchens and dining areas, and access to lounges, gyms, and other on-site amenities. Many high-end office spaces also provide support services such as receptionists, IT support, and cleaning services.
Security and Privacy
A high-end London office space offers exceptional security and privacy. These offices are equipped with advanced security systems, such as CCTV cameras, biometric access control, and 24/7 manned security.To ensure the safety of staff and assets. Privacy is also a key feature of high-end offices.With many providing private meeting rooms and phone booths for confidential discussions.
Flexibility
High-end London office spaces offer a high degree of flexibility.With a range of workspace options to suit the needs of businesses of all sizes. These include private offices, co-working spaces, virtual offices, and hot desking options. Many high-end office spaces also offer flexible leasing options, allowing businesses to adapt to changing market conditions.
Community and Networking
A high-end London office space provides businesses with the opportunity to network and collaborate with other like-minded individuals and companies. Many high-end office spaces host regular networking events, workshops, and seminars. Providing businesses with opportunities to build relationships, exchange ideas, and learn from industry experts.
Conclusion
A high-end London office space offers businesses an exceptional workspace solution that combines luxury, convenience, and flexibility. These offices are designed to create an environment that enhances productivity, creativity, and professionalism. Offering a range of facilities and amenities to support the needs of modern-day businesses. Whether you are a start-up, SME, or large corporation, a high-end London office space can provide you with the workspace and support you need to succeed in today’s competitive business world.
Business
How to Invest: A Comprehensive Guide for Financial Success

How to Invest: A critical component of accumulating money and ensuring a secure financial future is investing. It’s crucial to comprehend the basics of investing, regardless of your level of experience. This post will serve as thorough instruction on how to invest, including helpful insights, techniques, and advice to assist you in making wise investment choices. You may increase potential returns while lowering risks by refining your investing strategy. So let’s explore the investment world and discover how to put your money to work for you.
Set Clear Investment Goals
Setting goals is essential before beginning your investment path. Decide on your financial goals, such as supporting your child’s school, retiring early, or buying a home. You can decide your investing horizon, risk tolerance, and ideal asset allocation by setting specific goals. You may create a targeted investing plan that meets your needs by matching your investments with your ambitions.
Understand Different Investment Options
You must be knowledgeable about the numerous market investing possibilities if you want to invest wisely. Popular investment alternatives include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), real estate, and commodities. Every investing strategy has a unique amount of risk and possible reward. To make judgments depending on your level of risk tolerance and financial objectives, do your own research and education on these possibilities.
Diversify Your Portfolio
One important investment idea is diversification. Lowering risk entails distributing your assets across several sectors, geographic locations, and asset classes. You may lessen the effect that the success of any one investment has on your overall wealth by diversifying your portfolio. To create a portfolio that is well-balanced, think about investing in a variety of stocks, bonds, properties, and other assets.
Conduct Thorough Research
Do extensive study to understand the possible risks and benefits of any asset before investing. To make wise selections, consider past performance, market trends, and pertinent news. Utilize trustworthy investing journals, websites, and financial periodicals to learn more about particular businesses or industries.
Develop an Investment Strategy
Develop a unique investment plan based on your goals, risk tolerance, and research. Choose between being an aggressive stock trader who often buys and sells stocks or a passive investor who seeks to replicate the market’s performance over time. Your strategy should outline your asset allocation, investing time horizon, and procedures for monitoring and updating your portfolio.
Regularly Monitor and Rebalance Your Portfolio
Investment management is a continuous process that necessitates adjustments. Regularly assess your portfolio’s performance and compare it to your investing goals. Maintain the correct asset allocation by periodically rebalancing your portfolio by adding or selling assets. To make wise selections, keep an eye on market and economic trends.
Conclusion
The path to financial prosperity and freedom may be paved with prudent investing. You may start your financial adventure with confidence if you adhere to the instructions provided in this detailed handbook. Always remember to establish specific objectives, diversify your holdings, do extensive research, and create a unique investment plan. Regularly monitor your assets and make required adjustments to your portfolio. If you have patience, commitment, and the right information, you can effectively navigate the complex world of investing and achieve your long-term financial objectives.
-

 Fashion6 months ago
Fashion6 months agoHow To Style Earrings for a Night Out
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoWhat Can You Expect from a High-End London Office Space?
-

 Real Estate1 year ago
Real Estate1 year agoHow to Unlock the Benefits of Real Estate Investment in Pakistan
-

 Tech11 months ago
Tech11 months agoTMIIS Virtual Gateway: Opening New Horizons in Global Connectivity
-

 Digital Marketing2 months ago
Digital Marketing2 months agoHow to calculate CPM in digital marketing?
-

 Lifestyle1 year ago
Lifestyle1 year agoThe New Trend in Home Furnishings Teapoy and Wooden Sitting Stool
-

 General2 months ago
General2 months agoUnraveling the Mysteries of “λιβαισ”: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 Real Estate1 year ago
Real Estate1 year ago5 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Buying Property in Pawleys Island, SC
